Velocity Requirements for XP Dust
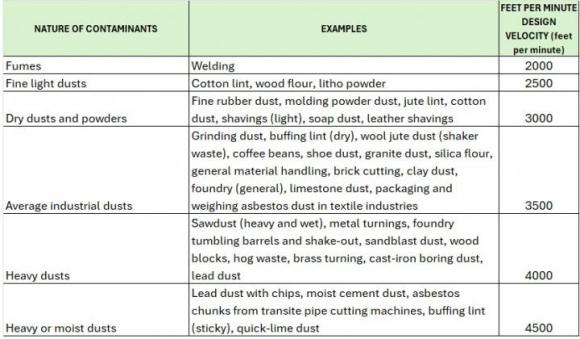
Minimum Conveying Velocities of common contaminants to prevent dust "laying down" in ducting

Conveying Velocity Requirements
The Class and Div requirements are only half of the picture
If the right amount of CFM isn't provided, then over time the duct will fill up with dust accumulation and eventually collapse. We take several factors into consideration to calculate how many CFM are required. Elbows and other resistance points are all taken into consideration to ensure effective and timely evacuation of the contaminants. .
NFPA Minimum Conveying Velocity for Common Contaminants
Capture Velocity Requirements
An ideal scenario for optimal operation is a capture velocity of 150 to 300 fpm.
Calculating CFM needed for ACH
CFM = (Room Volume × ACH) / 60
Step 1: Measure the room
First, you need to find the room's total volume in cubic feet.
- Length: Measure the length of the room in feet.
- Width: Measure the width of the room in feet.
- Height: Measure the ceiling height in feet.
Step 2: Calculate the room's volume
Multiply the room's dimensions to find its volume.
Step 3: Determine the required ACH
Air changes per hour (ACH) indicates how many times the air in a room is replaced each hour. Recommended ACH values vary by room type: Bedrooms (5–6), Living Rooms (6–8), Kitchens (7–8), Bathrooms (7–8), and Laundry Rooms (8–9).
Step 4: Calculate the CFM
Use the room's volume and the chosen ACH in the CFM formula.
Example calculation
For a 12 ft by 14 ft living room with a 10 ft ceiling and a target ACH of 6: